National News
10 Things to know about ex-President Muhammadu Buhari
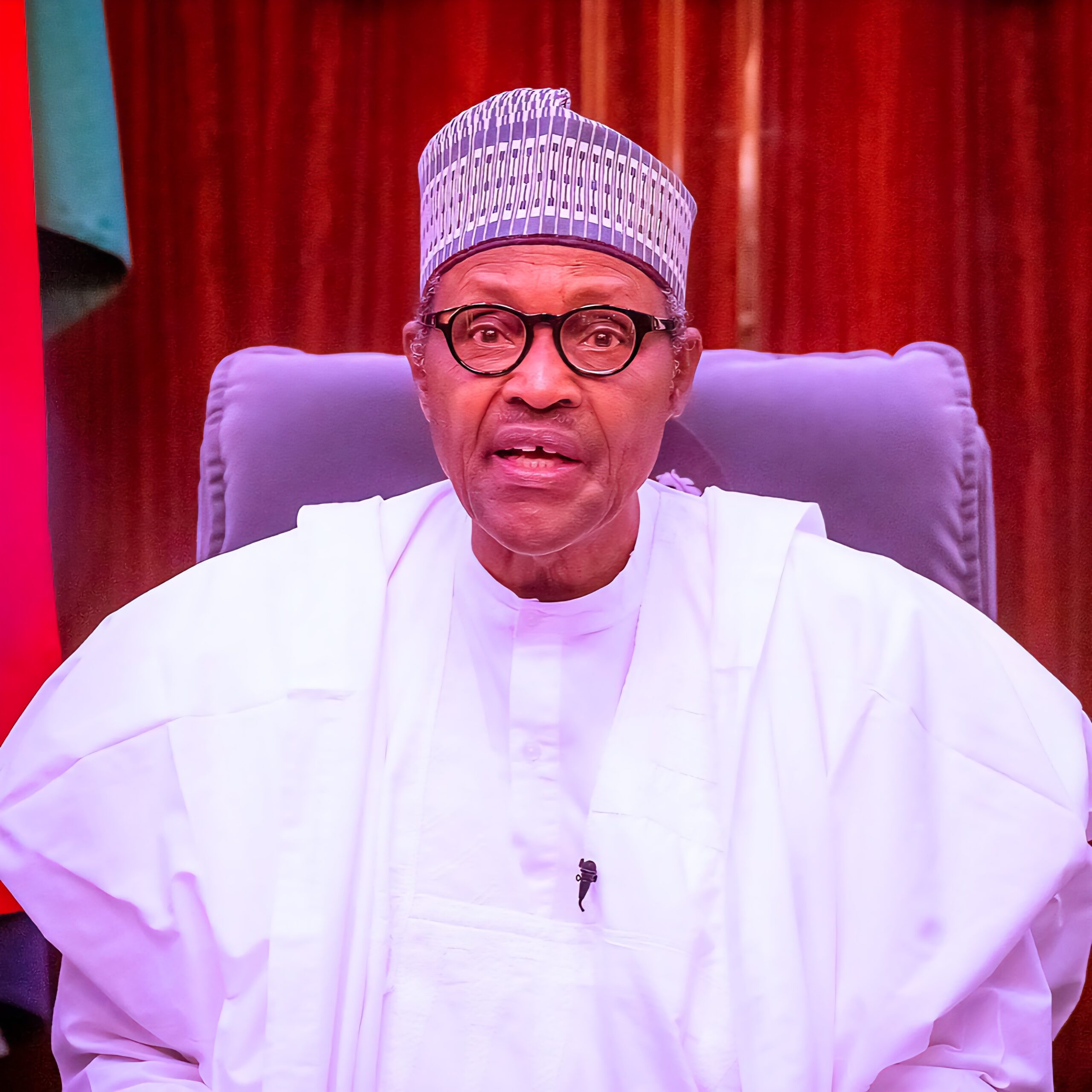

Muhammadu Buhari was one of Nigeria’s most influential and controversial leaders, whose career shaped the country’s military and political history for over five decades.
From serving as a military Head of State in the 1980s to becoming a democratically elected president, Buhari was known for his tough stance on corruption, national security, and discipline.
He remained a major political figure in Nigeria even after leaving office in 2023.
Buhari passed away on July 13, 2025, in a London hospital after battling a protracted illness.
His death marked the end of an era for one of Nigeria’s longest-standing public figures, whose leadership left a lasting impact on the country’s governance and public life.
Here are 10 important things to know about the late ex-President Muhammadu Buhari:
1. He Was Born in Daura, Katsina State Muhammadu Buhari was born on December 17, 1942, in Daura, a town in Katsina State, Northern Nigeria. He was the twenty-third child of his father, Mallam Hardo Adamu, a Fulani chieftain.
Raised in a devout Muslim family, Buhari grew up with strong traditional and Islamic values, which would later shape his conservative leadership style and public persona.
2. Buhari Had a Distinguished Military Career Before venturing into politics, Muhammadu Buhari had an illustrious career in the Nigerian Army.
He enlisted in 1961 and was trained in several prestigious military institutions, including the Nigerian Military Training College (now Nigerian Defence Academy), the Mons Officer Cadet School in Aldershot, England, and the Defence Services Staff College in India.
He rose steadily through the ranks and was involved in several military operations during Nigeria’s civil war (1967–1970).
His military discipline and reputation for no-nonsense leadership earned him significant respect among his peers.
3. Buhari Served as Nigeria’s Military Head of State (1983–1985) On December 31, 1983, Muhammadu Buhari became Nigeria’s military Head of State following a coup that overthrew the civilian government of President Shehu Shagari.
His administration was characterized by a tough anti-corruption drive, rigid enforcement of discipline, and controversial economic policies.
He launched the War Against Indiscipline (WAI), aimed at restoring societal order and accountability.
However, his regime was criticized for human rights abuses, press censorship, and economic hardship, leading to his eventual overthrow in another military coup led by General Ibrahim Babangida in August 1985.
4. He Contested for Presidency Four Times Before Winning After retiring from military service, Buhari transitioned into politics.
He contested for Nigeria’s presidency under different political parties in 2003, 2007, and 2011, but lost all three elections.
Undeterred, he contested again in 2015 under the All Progressives Congress (APC) and made history by becoming the first opposition candidate to defeat an incumbent president, Goodluck Jonathan, in Nigeria’s democratic history.
He was re-elected for a second term in 2019 after defeating Atiku Abubakar of the People’s Democratic Party (PDP).
5. Buhari’s Presidency Focused on Anti-Corruption, Security, and Economic Recovery Buhari’s civilian presidency was anchored on three core priorities: fighting corruption, combating insecurity, and revamping the economy.
He launched notable anti-corruption campaigns, leading to high-profile arrests and asset recoveries. On security, he prioritized the fight against the Boko Haram insurgency in the North-East, though challenges persisted.
Economically, Buhari’s administration faced multiple recessions, currency devaluation, and inflation, with mixed reviews on policy effectiveness.
His government also emphasized infrastructure development through rail, road, and agricultural projects.
6. He Was Widely Criticized for Human Rights and Press Freedom Issues Despite his anti-corruption stance, Buhari’s administration faced frequent criticism for stifling press freedom, clamping down on dissent, and restricting civic space.
Human rights groups accused the government of unlawful detentions, police brutality, and the suppression of protests, notably during the #EndSARS protests in October 2020, where security forces opened fire on unarmed protesters at the Lekki Toll Gate in Lagos, an incident that drew global condemnation.
7. Buhari Maintained a Reputation for Personal Integrity Regardless of criticisms about his government’s performance, Buhari was consistently viewed as a leader of personal discipline, modest lifestyle, and incorruptibility.
Even his political opponents and international observers often acknowledged his reputation for financial honesty.
Buhari reportedly declared his assets publicly before assuming office in 2015, although controversies surrounded asset disclosures of other officials in his government.
8. He Spent Extended Periods Abroad for Medical Treatment A significant feature of Buhari’s presidency was his recurrent medical trips to the United Kingdom.
Between 2017 and 2019, he spent over 150 cumulative days abroad seeking treatment for undisclosed ailments, prompting concerns about transparency, governance gaps during his absences, and the state of Nigeria’s healthcare system.
His prolonged absences occasionally triggered speculations about his health and capacity to govern.
9. Buhari Is Married to Aisha Buhari Muhammadu Buhari is married to Aisha Buhari (née Halilu), who served as Nigeria’s First Lady from 2015 to 2023.
Aisha, a trained cosmetologist and author, gained national attention for her outspoken criticisms of some government officials and policies during Buhari’s tenure.
The couple has five children together. Buhari was previously married to Safinatu Yusuf, with whom he had five children, before their separation in 1988.
10. Buhari Remains a Major Political Influence in Northern Nigeria Even after leaving office in May 2023, Muhammadu Buhari continues to wield considerable political influence, especially in Northern Nigeria.
As a former military leader and two-term civilian president, his endorsement or opposition carries weight in Nigeria’s political landscape.
He has largely refrained from active political commentary since leaving office but remains a respected elder statesman within the ruling APC and the broader Nigerian polity.
Conclusion
Muhammadu Buhari’s life and career span significant periods in Nigeria’s modern history, from military coups and civil war to democratic transitions and insurgency.
Loved by some for his discipline and anti-corruption posture and criticized by others for authoritarian tendencies and economic challenges, Buhari remains a complex, consequential figure in Nigeria’s political narrative.
-

 Uncategorized12 hours ago
Uncategorized12 hours agoEmpowering Women: Economic, social necessity –Faleye
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoIran warns protesters supporting foreign enemies will be treated as ‘enemies’
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoKano Governor sacks Head of Service Abdullahi Musa
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTraders shut down Lagos International Trade Fair Complex over takeover concerns
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoFlying Eagles midfielder Daniel Daga sentenced to six months in Norway
-

 News12 hours ago
News12 hours agoCelebrating Funke Ishola: A Trailblazer and pillar of empowerment
-

 World News1 day ago
World News1 day agoIran’s new Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei injured but safe, official says
-
 National News1 day ago
National News1 day agoTinubu nominates Lamido Yuguda as CBN Deputy Governor






































